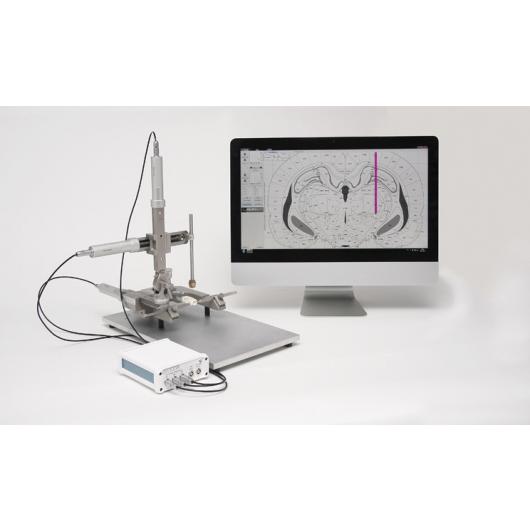
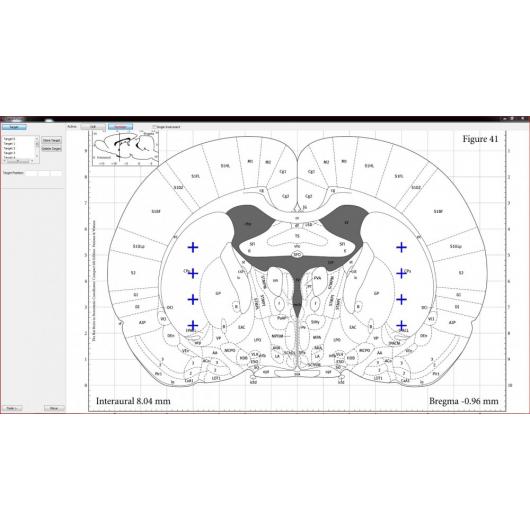
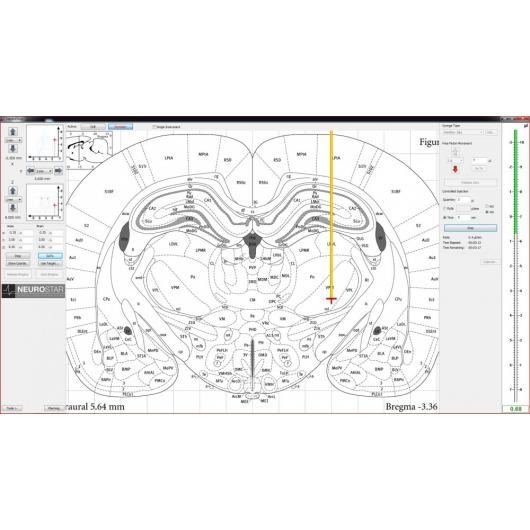
Robot stereotaktyczny – StereoDrive
Neurostar jest wynalazcą i jedynym na świecie producentem robotów stereotaktycznych StereoDrive. Wykorzystując ramę StereoDrive możesz przeprowadzać eksperyment bez konieczności ręcznego manipulowania ustawieniami. StereoDrive jest wyposażony w silniczki sterowane komputerowo, które pozycjonują sondę w punkcie o parametrach ustalonych przez eksperymentatora. Integracja systemu z atlasem mózgu i intuicyjna kontrola ruchów zdecydowanie wpływa na olbrzymią dokładność, wysoką przepustowość badań elektrofizjologicznych i iniekcji stereotaktycznych.
Zalety stereotaksji StereoDrive
- komputerowa kontrola
- integracja z atlasem mózgu
- automatyczne skalowanie atlasu w odniesieniu do punktów bregma i lambda
- korekcja pochylenia głowy
- ustawienie punktu bregma
- ustawienie kątów
- uniknięcie błędów ludzkich dzięki pełnej automatyzacji zabiegów
- ogromna precyzja
- oszczędność czasu ze względu na wykonywanie precyzyjnych zabiegów
- wysoka przepustowość badań
- planowanie eksperymentu
- definiowanie i przechowywanie celów eksperymentu w oprogramowaniu
- intuicyjna nawigacja w oprogramowaniu
2013
Prefrontal Activity Links Nonoverlapping Events in Memory.
Gilmartin, M. R., Miyawaki, H., Helmstetter, F. J., & Diba, K. (2013)
The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(26), 10910-10914.
Babaei, P., Tehrani, B. S., & Alizadeh, A. (2013)
Journal of Behavioral and Brain Science, 3, 156-161.
Subcortical effects of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in the rat.
Bolzoni, F., Bączyk, M., & Jankowska, E. (2013)
J. Physiol. 2013 Aug 15;591(Pt 16):4027-42. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.257063. Epub 2013 Jun 17.
Bell, L. A., Bell, K. A., & McQuiston, A. R. (2013)
Neuropharmacology. 2013 Oct;73:160-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.05.026. Epub 2013 Jun 5.
Ali, I., O’Brien, P., Kumar, G., Zheng, T., Jones, N. C., Pinault, D., O’Brien, T. J. (2013).
PLOS ONE, 8(6), e66962.
The toxicity of antiprion antibodies is mediated by the flexible tail of the prion protein.
Sonati, T., Reimann, R. R., Falsig, J., Baral, P. K., O’Connor, T., Hornemann, S., Aguzzi, A. (2013)
Nature, 501(7465), 102-106.
Albéri, L., Lintas, A., Kretz, R., Schwaller, B., & Villa, A. E. (2013)
Journal of Neurophysiology, 109(11), 2827-2841.
2012
Clarner, T., Diederichs, F., Berger, K., Denecke, B., Gan, L., Van der Valk, P., Kipp, M. (2012).
Glia, 60(10), 1468-1480.
Feng, L., Sametsky, E. A., Gusev, A. G., & Uteshev, V. V. (2012)
Journal of Neurophysiology, 108(7), 1884-1894.
2011
Girardet, C., Bonnet, M. S., Jdir, R., Sadoud, M., Thirion, S., Tardivel, C., Troadec, J. D. (2011)
Toxicological Sciences, 124(1), 179-191.
2010
A26 Transgenic miniature pig as an animal model for Huntington’s disease.
Baxa, M., Juhas, S., Pavlok, A., Vodicka, P., Juhasova, J., Hruška-Plocháň, M., Motlik, J. (2010).
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A8-A9
Yu, L., Metzger, S., Clemens, L. E., Ehrismann, J., Ott, T., Gu, X., Nguyen, H. P. (2010).
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A9.
Brooks, S., Jones, L., & Dunnett, S. B. (2010). A29
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A10.
Hruška-Plocháň, M., Juhas, S., Juhasova, J., Galik, J., Miyanohara, A., Marsala, M., Motlik, J. (2010).
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 81(Suppl 1), A9-A9.